About breakthroughs in 2017 in technology and science
The year 2017 has become for the world a technological point of no return. Innovations have appeared even in conservative industries, where they began to play a decisive role in the competition. Let's talk about the achievements in business and science for 2017, which will change our future.
Solar energy

From 2005 to 2015, the cost of generating solar energy fell by 6 times. Soon, innovations will allow solar power stations to bypass the efficiency and efficiency of conventional thermal power plants. But there is an obstacle to the development of solar energy - high cost and low efficiency of the panels: they only strengthen visible light from red to purple. Recent developments of scientists from the US prove that the level of productivity of photocells can be raised more than 2 times. They created a prototype of a 'hot solar battery', in which, in addition to the photocell, there is also an 'absorber-emitter'. So the upper layer, consisting of carbon nanotubes, completely absorbs the energy of the directional solar flux and converts its most part into thermal energy. At 1000 degrees the emitter based on the photonic crystal gives energy further, turning it again into a sunbeam, but in a narrower spectrum suitable for the panel. So far, batteries can only work in a vacuum, but scientists are working on a scheme to simplify the technology.
In 2017 it became clear: affordable and cheap solar energy is able to solve the issues of generation of heat and electricity, as well as reduce the shortage of drinking water. This innovation is already acquiring commercial outlines. In the autumn, the American start-up Zero Vass Water launched sales of devices based on solar panels that can absorb water from the air. Spongy nanomaterials are able to capture water molecules and from the atmosphere with a moisture level of up to 20%. And the energy received from the sunlight, allows you to separate water from the absorbent and make it suitable for drinking. The device, equipped with 2 panels, can produce 5 liters water per day. Given the market value of $ 4.5 thousand, including installation, it can fully pay off on average over 5 years. Zero Mass Water intends to stake on its social projects. For example, establish their systems in African schools and refugee camps in the Middle East.
Agricultural revolution

Meet the new iron farmers with propellers! The agrarian industry has actively and universally began introducing ultra-modern tools 'precise' farming. Agrarians have adopted smart gadgets to match the arsenals of James Bond. Now they plow the ground under the control of unmanned robots with radio control, make a marking of arable land, using GPS navigation and graze cattle with the use of 'smart' video cameras that can identify complex objects. For example, the autonomous robot Swagbot developed by Sydney's engineers is able to replace both the veterinarian and the shepherd dog. The device collects the animals in the herd and drives them away in the right direction, and also monitors their health with the help of special sensors.
In agriculture, 'heavy' technologies for soil modeling, machine learning and Big Data analysis algorithms began to be used. All these tools are designed to solve purely applied tasks: to improve product quality and yield of fields, to reduce the consumption of pesticides, water and fertilizers. And most importantly, to reduce manual labor.
The drones niche is also developing very rapidly. The company PricewaterhouseCoopers estimated this product at 32.5 billion and predicts its rapid growth. UAVs are capable of sowing crops, fighting pests, watering and pollinating fields, analyzing the state of the crop and the soil. So the drone developed by the British authors of the startup BioCarbon Engineering can plant 100 thousand trees a day. Compared with standard technologies, this is 85% cheaper and 75% faster. Such drones are already restoring forest tracts in Ireland and Australia.
In 2017, a Swiss company with Russian roots Gamaya offered to the market drones to monitor sugar cane and soy crops. The devices monitor whether plants do not dry up, whether they suffer from pests and give the farmer advice on acceptable corrective methods for processing their land. More than 6 million euros have already been invested in this start-up.
Quantum computers
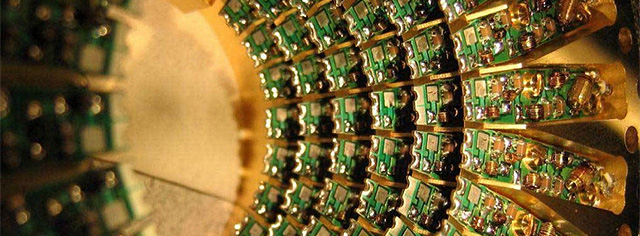
The desire to create super-powerful and ultrafast computing machines, operating on the principle of quantum computing, was agitated by scientists for about 50 years. But only in 2017 this theory began to find the real outline. And the 'futurists' promised 'quantum leap' is the matter of tomorrow. More than 50 research groups around the world are creating of powerful computing machines using a variety of technologies and approaches. Someone using 'cold atoms,' somebody is superconductors. There are companies (for example, D-Wave) that already supply adiabatic systems that are capable of solving narrow tasks, but which have not yet been able to handle some quantum algorithms.
But Harvard, Google and IBM began testing 50- and 51-qubit full-fledged quantum machines, capable of easily circumventing the speed of computing modern supercomputers, even the famous Watson.
Do the quantum successes of change promise to business and ordinary people? Of course! Quantum calculations allow developing various branches of the economy. In pharmaceuticals, these devices will simulate complex molecules of all kinds of substances, predict their reactions and anticipate their behavior. You will no longer need to invest billions in pre-clinical studies of medicines. In chemistry, they will establish the production of new strong polymers (in aircraft and automotive industry). In the power industry - will create more productive solar cells for solar panels. In production, transport, trade, logistics - will help to optimize all processes and get rid of unnecessary downtime. In computer science - accelerate machine learning and contribute to the creation of artificial intelligence. All these innovations are a matter of 5-10 next years.
Unmanned trucks

Technologies of autonomous driving find application in the corporate sphere much faster than in the consumer. In 2017, many companies announced the beginning of work on the creation of autonomous trucks which will make driving safer and reduce transportation costs. The Israeli start-up Otto is already testing on the roads 7 (seven) of its electro trucks. Similar projects are being developed by Volvo, Peterbilt, Daimler. In autumn, Tesla introduced its automatic truck. It is equipped with an autopilot, which allows the large truck to move in tight columns. In such cargo chains, the aerodynamic resistance is sharply reduced, which is why fuel consumption is falling. Movement in a tight column allows you to reduce costs by 10%, and in electro trucks, in comparison with diesel trucks - in 2 times. Such drones will be used both for the delivery of goods, and for covering the 'last mile'.
Delivery of goods from the warehouse to the end user is the bottleneck in the logistics chain of the e-commerce sector. In the summer of 2017, the British start-up Ocado Technology tested its CargoPod electric van in London. The car is equipped with 8 closed compartmentalized compartments. Approaching the place of delivery, he sends an alert to the buyer about his arrival on the smartphone, then parked, highlights the necessary office and waits for the recipient to pick up his goods. Loading the van does not need human participation. The processing of the order, the search for the goods in the warehouse, packing and shipping are carried out by robots.
Experts say that in the next 5-10 years, autonomous trains, trucks and public transport will become part of everyday life. It remains to decide the issue of finding employment for millions of truckers, who will be left without autopilots.
Human Cell Atlas
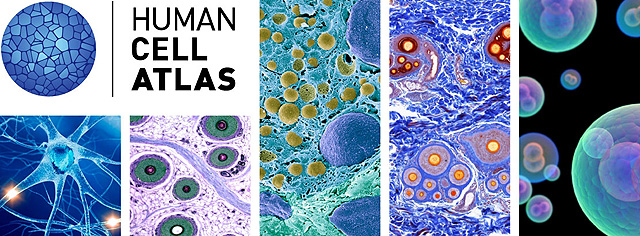
In 2016 scientists of America, Japan, Great Britain, Israel, Holland and Sweden launched a large-scale project Human Cell Atlas. He is able to decipher, locate and describe the properties of each cell of the human body. A detailed map of cells makes it possible to understand the development of various diseases and find new effective methods for their treatment. The project was supported by the founder of Facebook and his wife, having allocated a grant of $ 600 million to the California-based research center Biohub, which intends to bring together researchers in this field from the University of San Francisco, Berkeley and Stanford.
In 2017, the project brought the first results. Scientists of the University of Sweden have completed work on creating a detailed map of proteins in the human body, over which they have worked for 10 years. They were localized more than 12 thousand proteins. At the same time, many species were systematized and described for the first time. And in November, published the first three-dimensional sketch of the small intestine cell map. It includes more than 53 thousand cells and looks amazing: a cluster of colored dots is similar to a photograph of cosmic nebulae.
It is in this way - the organ behind the organ, the cell behind the cell, the scientists want to 'map' the human body further. This method became available only in recent years, after the development of the technology of DNA sequencing of single cells 8 years ago. Each cell in the body contains approximately the same set of genes, but the sequence of 'switched off' and 'switched on' cells is different. This sequence determines the cellular nature: it 'programs' it to perform special functions - to send signals to the brain or to produce hormones. At present, genetic engineers and biotechnologists isolate individual cells, 'reading the sequence of RNA and DNA to describe the structure. Using innovative methods of CRISPR technology, which is designed to edit the genome, each cell in the cell is assigned a fluorescent label to determine its location. It 'highlights' the active protein when attacking various external agents (viruses, bacteria).
Work on the creation of an atlas will take 5-8 years. The data will allow us to better understand the mechanisms of development of rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, HIV infections, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's, etc.
The information accumulated within the framework of the project will be kept in the public domain so that scientists can use it as soon as possible.
All articles of the project

